DESPITE INSULIN THERAPY, MOST PATIENTS WITH TYPE 1 DIABETES (T1D) DO NOT ACHIEVE THEIR GLYCAEMIC GOAL
The majority of patients were above target HbA1c levels.1
A high proportion of patients outside the United States were also insufficiently controlled
- In the EURIODIAB study, of the 2,764 patients from 31 centres in 16 European countries, the mean HbA1c was 8.4%3
HYPOGLYCAEMIA IS A MAJOR RISK AND FEAR FOR PATIENTS WITH T1D
Intensification of insulin therapy is associated with an increased risk of severe hypoglycaemia
- The Incidence of severe hypoglycaemia was approximately 3x higher in the intensive therapy group vs the conventional therapy group in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (P<0.001)4
Controlling glycaemic variability is an important part of managing HbA1c levels
- Time out of range places patients with T1D at risk of hypoglycaemia and postprandial hyperglycaemia.* It can also impact their day-to-day quality of life5†
*Time in range is considered to be time spent within 70–180 mg/dL.5
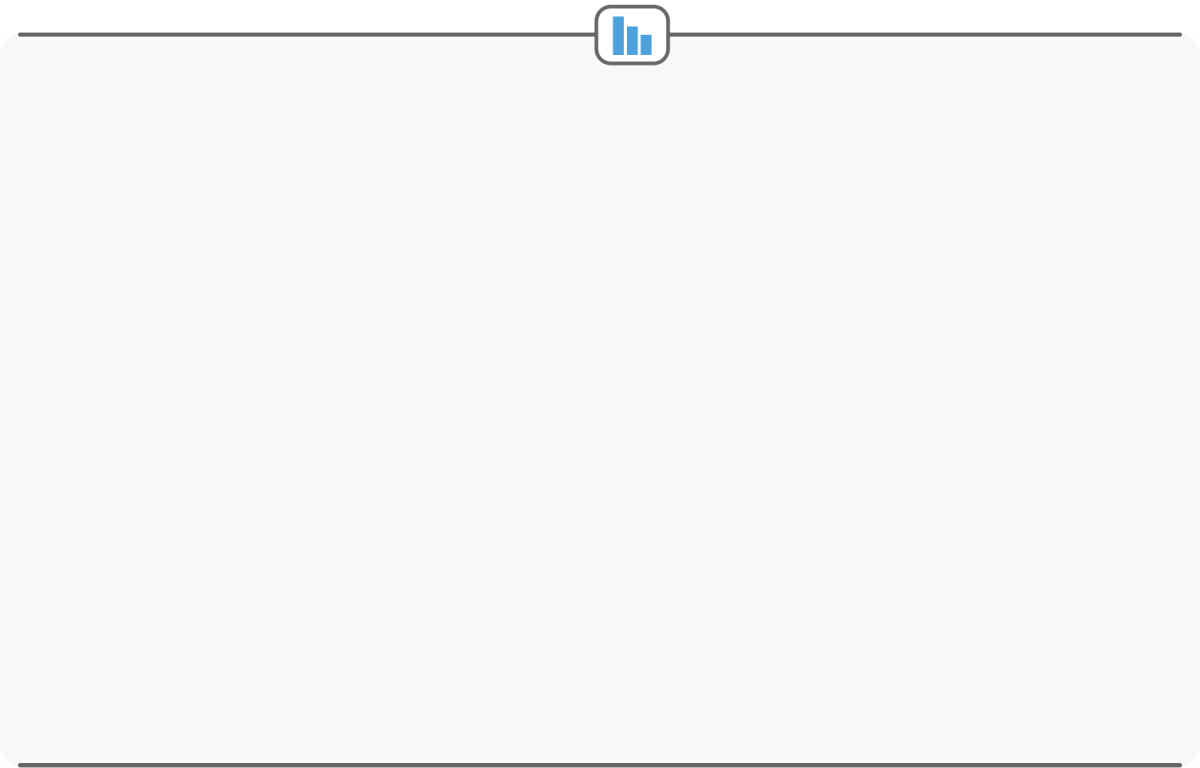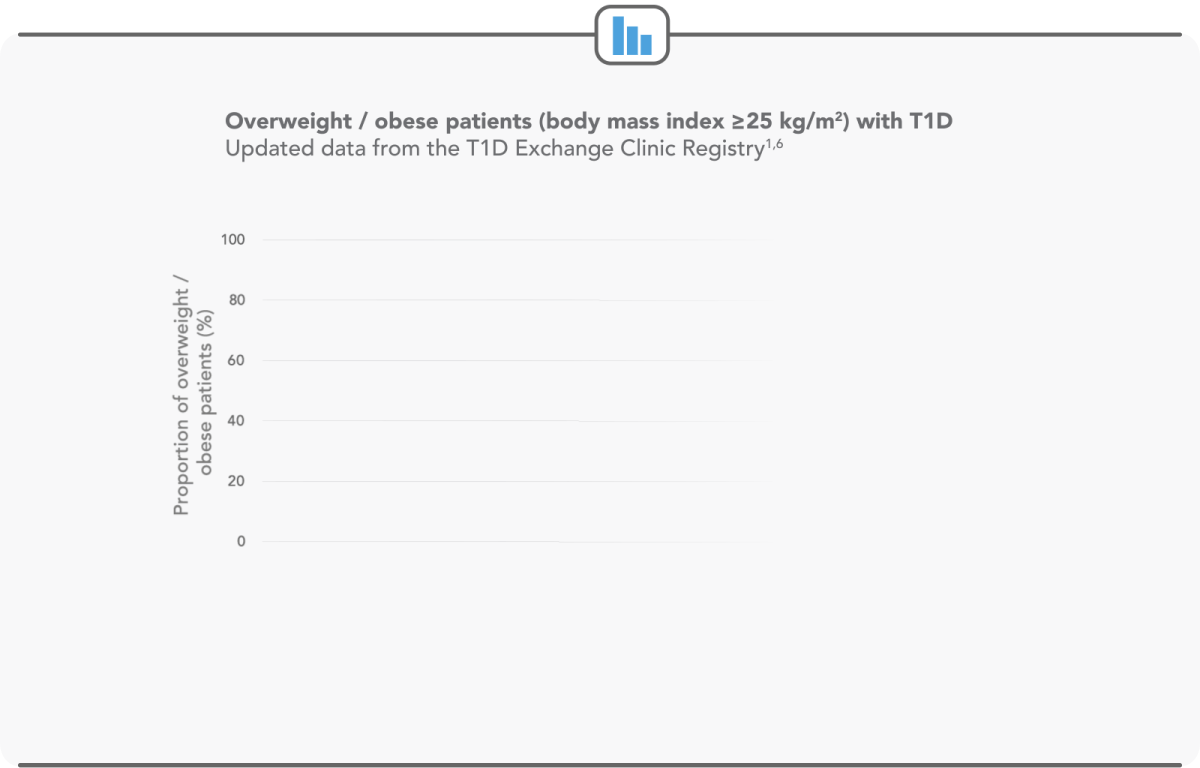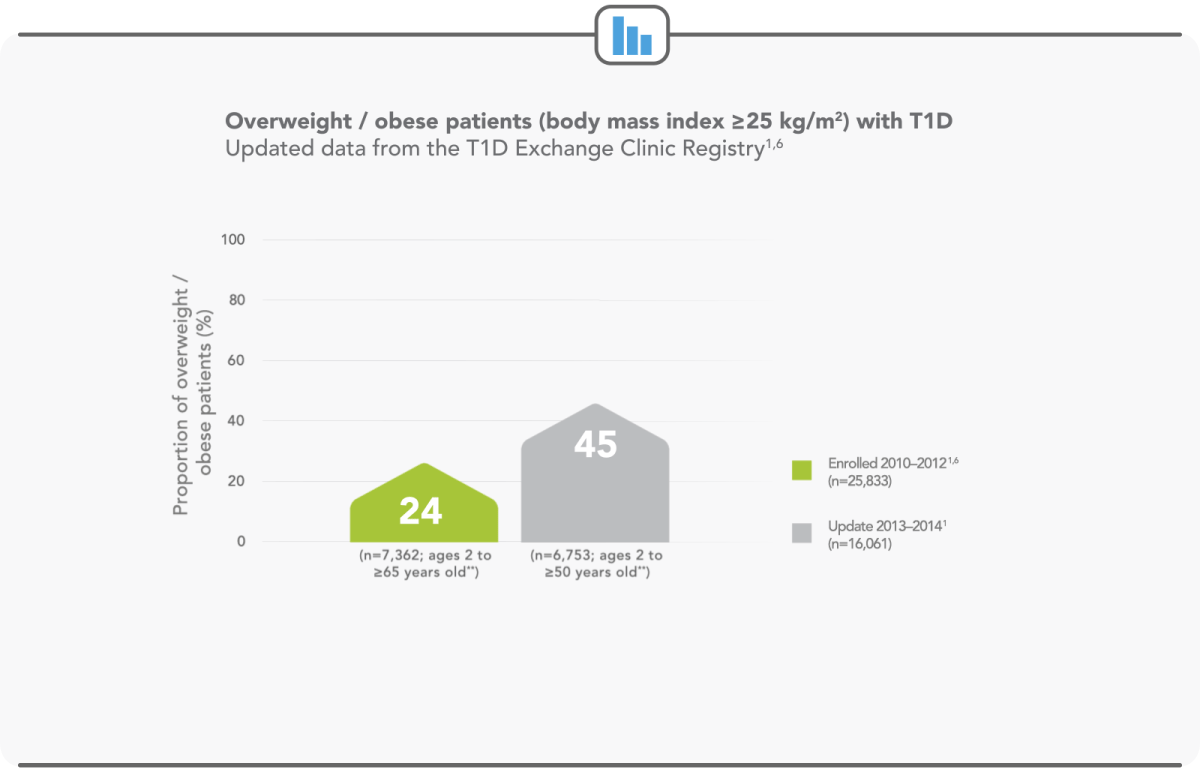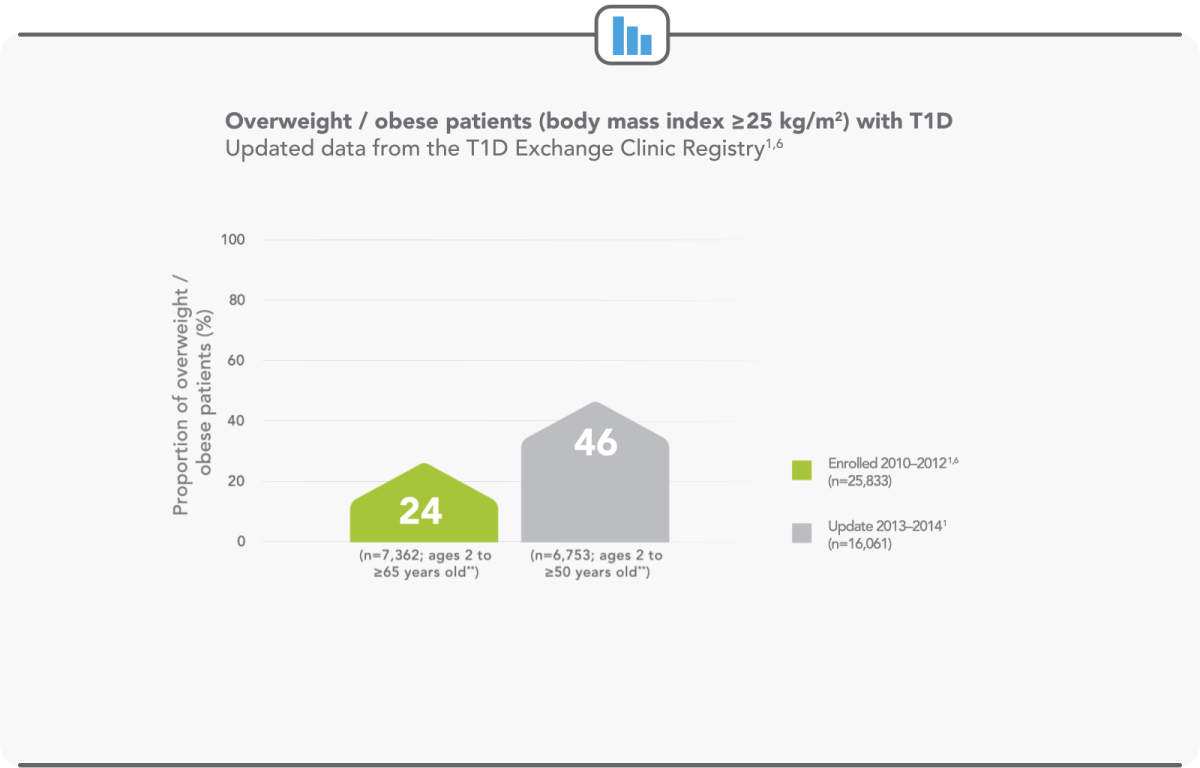
WEIGHT GAIN IS A GROWING ISSUE AMONG THE T1D POPULATION
Between enrolment (2010–2012) and the updated data (2012–2014), the percentage of overweight or obese patients increased from 24% to 46%1,6
**Forxiga is only indicated in adult T1D patients with body mass index ≥27 kg/m2.7
References:
- Miller KM, Foster NC, Beck RW, et al. Current state of type 1 diabetes treatment in the U.S.: updated data from the T1D Exchange clinic registry. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(6):971–978.
- American Diabetes Association. 6. Glycemic targets: standards of medical care in diabetes— 2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(suppl 1):S55-S64.
- Schoenaker DA, Simon D, Chaturvedi N, et al. Glycemic control and all-cause mortality risk in type 1 diabetes patients: the EURODIAB prospective complications study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(3):800–807.
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(14):977–986.
- Danne T, Nimri R, Battelino T, et al. International consensus on use of continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(12):1631–1640.
- Beck RW, Tamborlane WV, Bergenstal RM, et al. The T1D Exchange clinic registry. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(12):4383–4389.
- Forxiga. Summary of Product Characteristics. 2019. AstraZeneca.